Braking units – Overview
How does an electronic motor braking device work?
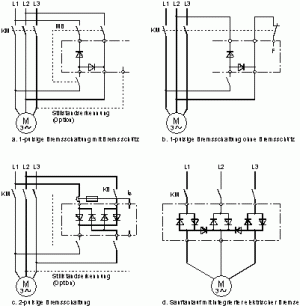
An electronic motor braking device works on the principle of feeding direct current into the stator winding of three-phase induction motors. This generates a standing magnetic field which inhibits the movement of the squirrel-cage rotor.
The braking effect depends on the size of the braking current. This is generated by rectifying the supply voltage.
The use of thyristors with phase control allows the braking torque to be set over a wide range.
DC braking causes a heating up of the motor.
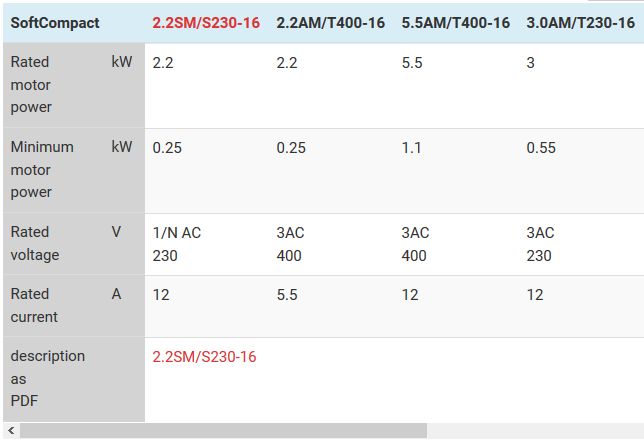
In soft start and braking units or combi units, soft start and DC braking are represented in one unit or device combination. This enables very compact, universally applicable solutions.
Applications
Electronic braking devices enable wear-free braking of three-phase asynchronous motors and offer a robust alternative to mechanical brakes. Here you will find practice-related application examples:

Braking units
2.2 – 7.5 kW
LEKTROMIK® B1
Features
- AC 230 V, AC 400 V, AC 480 V
- Single-pulse or partially or semi-controlled rectification with truncated half-wave
- Braking torque and braking time-out separately adjustable
- Mounting on 35 mm DIN rails
- Side-by-side mounting
- Easily retrofitted
- Can be used without braking contactors
- Suitable as a combined soft start and brake using the soft start SoftCompact
Applications
- Woodworking machines
- Grinding machines
- Conveyor belts with long running down times
- Vibration sources
- Centrifuges
- Test rigs
Special versions, e.g. 480 V, please inquire.

Braking units
15 – 200 kW
LEKTROMIK® B4
Features
- AC 220 – 500 V
- Two-pulse or fully controlled rectification with truncated full-wave
- Braking torque and braking time-out
- Separately adjustable
- Detection of zero-speed
- Operation without braking contactor possible
- Suitable as a combined soft start and brake using the electronic soft start LEKTROMIK® S2 / SD2
- Limiting of maximum braking current
Applications
- Woodworking machines
- Vibration motors
- Roller-table drives in steel plants
- Machines with high inertia, e.g. mills, compactors, centrifuges
Up to 90 kW UL-certified for the USA and Canada.

 All KIMO® braking units in an overview
All KIMO® braking units in an overview