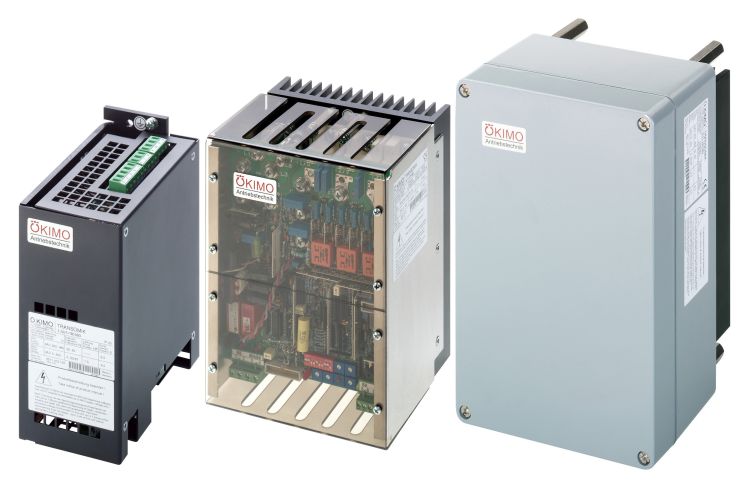
What is a soft starter?
A soft starter is a device for electronic motor control. It enables three-phase induction motors to start and stop smoothly.
The motor voltage is set by a phase control based on a ramp function. However, the supply frequency of the motor remains identical to the mains frequency.
With a soft start, the initial voltage (=starting torque) and the voltage rise (= acceleration) can be set.
With the soft stop, the voltage is reduced with a ramp function.
Typical areas of application are fans, conveyor belts and pumps.
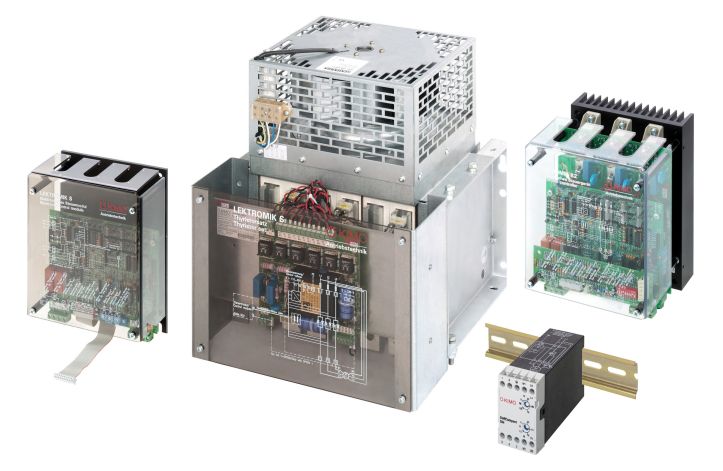

How works a braking device?
An electronic motor braking device works on the principle of direct current injection. It is intended for use with three-phase induction motors.
The direct current is induced in the stator winding of a three-phase induction motor. The static magnetic field generated in this way inhibits the movement of the squirrel cage and thus brakes the motor.
The braking effect itself is dependent on the size of the braking current. This is generated by rectifying the supply voltage.
If you also use thyristors with phase control, you can now freely set the braking torque over a wide range.
It is important to note that DC braking causes the motor to heat up.
Typical areas of application are woodworking machines, grinding machines, conveyor belts and centrifuges.
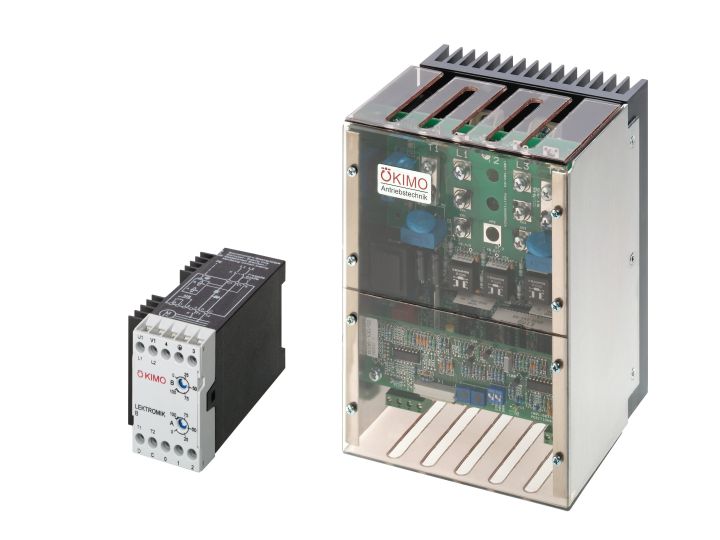

In soft starting / braking devices or combination devices or soft starting and braking device combinations, soft starting and DC braking are combined in one device.
This enables very compact, universally applicable solutions.
In addition to being used in woodworking machines and grinding machines, machines with long deceleration times can be braked here.

How works a voltage controller?
A voltage controller works in a similar way to a soft starter.
A soft starter controls the motor voltage to the full until the end of run-up.
Instead, a voltage controller remains – depending on the setpoint specification – in the partially or fully controlled range.
This allows the user to regulate the motor torque himself over a wide range.
Typical areas of application are fan controls and lighting controls. It can also be used as a power controller for electrical heating.
How works a braking chopper?
A braking chopper or chopper is connected to a DC link.
Its task is to limit the voltage in this DC link.
This is done by switching a resistor in a clocked mode when a set braking voltage is reached. Depending on the series, this can be an internal or external resistor.
A braking chopper is typically used together with a frequency converter for demanding braking tasks.
This can be a permanent brake or it is used to protect regenerative frequency converters in the event of a power failure.
Areas of application are drives for conveyor technology, travel and lifting applications or drives that have to be braked quickly.
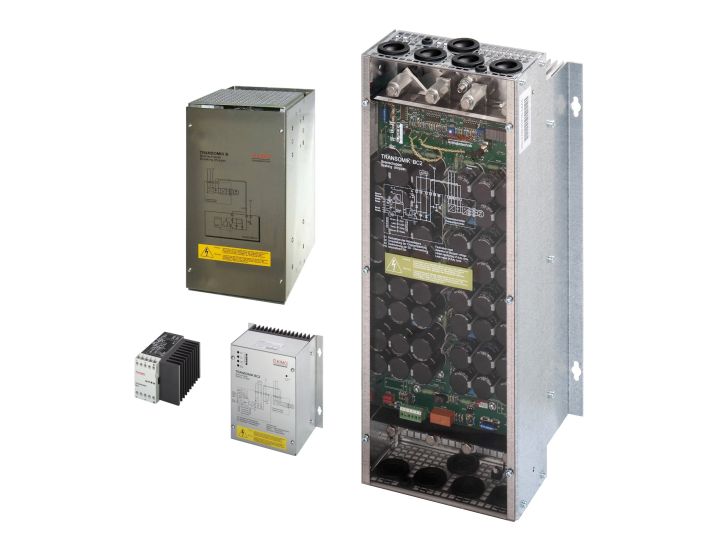

How works a frequency inverter?
A frequency inverter is the appropriate motor control device when working with continuous speed adjustment.
The difference to the soft starter lies in the handling of the frequency.
While a soft starter works with a constant frequency, the frequency inverter does not operate the motor rigidly on the mains with a constant frequency, but rather it regulates both the operating voltage and the operating frequency. The motor can thus be operated energy-efficiently over a wide speed range.
A regenerative frequency converter also offers the possibility of recovering the braking energy and feeding it back into the network.
Typical areas of application are refrigeration machines, conveyor systems and positioning drives with cyclical start-ups and braking.